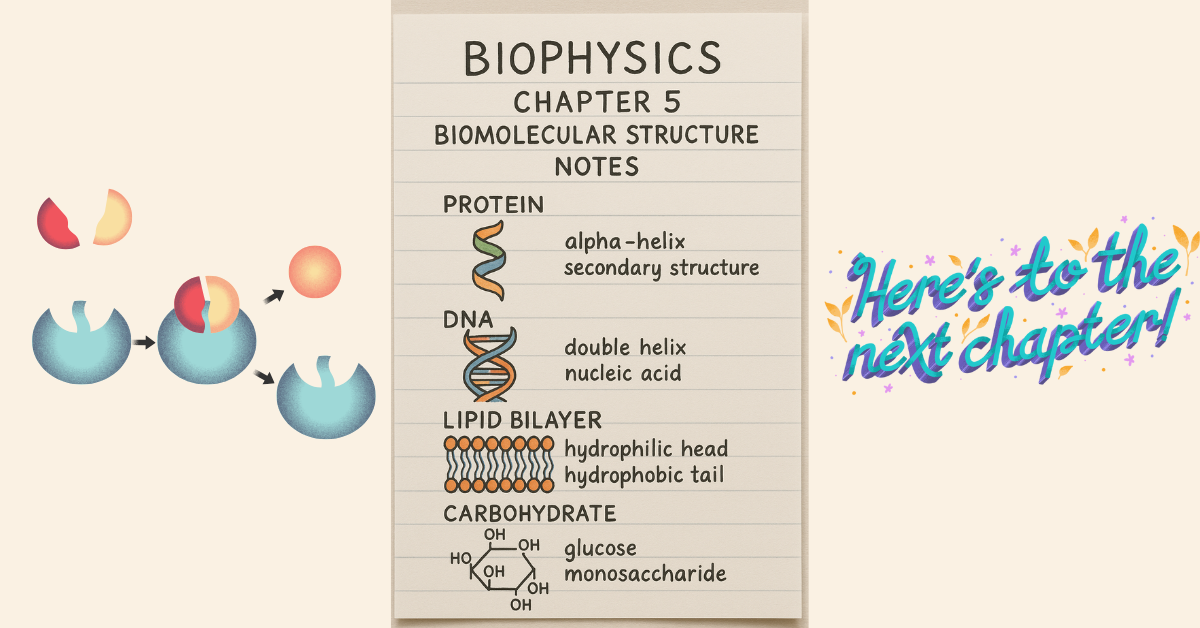
Biophysics Chapter 5 Biomolecular Structure Notes
Notes Biophysics Chapter 5: Biomolecular Structure
In the realm of biophysics, understanding the structure of biomolecules is fundamental to grasping how life functions at a molecular level. Biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates are the building blocks of all living organisms, and their unique structures dictate their biological roles and interactions.
What Are Biomolecules?
Biomolecules are organic molecules that play critical roles in the structure and function of cells. The four major classes are:
-
Proteins: Responsible for catalyzing reactions (enzymes), providing structural support, and regulating cellular processes.
-
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA store and transmit genetic information.
-
Lipids: Make up cellular membranes and store energy.
-
Carbohydrates: Provide energy and serve as structural components.
Protein Structure: The Basis of Function
Proteins are perhaps the most structurally diverse biomolecules. Their function depends heavily on their shape, which is organized into four levels:
-
Primary structure: The linear sequence of amino acids.
-
Secondary structure: Local folding into alpha helices and beta sheets due to hydrogen bonding.
-
Tertiary structure: The overall 3D folding driven by interactions between side chains.
-
Quaternary structure: Assembly of multiple protein subunits into a larger complex.
Each structural level is vital for the protein’s stability and function. Misfolded proteins can lead to diseases such as Alzheimer’s or cystic fibrosis.
Nucleic Acids: The Blueprint of Life
DNA’s famous double helix structure was a landmark discovery in molecular biology. This elegant twisted ladder shape allows DNA to compactly store genetic information while enabling replication and transcription. RNA, structurally similar but usually single-stranded, plays key roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
The Importance of 3D Structure
Biomolecules are not static; they undergo dynamic conformational changes that allow them to interact with other molecules, catalyze reactions, and transmit signals. Advanced techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy have helped scientists uncover these intricate structures.
Why Does Biomolecular Structure Matter?
Understanding biomolecular structure is crucial in fields ranging from drug design to genetic engineering. For example, many drugs work by binding to specific protein sites, altering their activity. Insights into molecular structure guide researchers in developing targeted therapies with fewer side effects.
Conclusion
The study of biomolecular structure bridges biology, chemistry, and physics, providing deep insights into how life works at its most fundamental level. As we continue to uncover the complexities of these molecules, we pave the way for innovations in medicine, biotechnology, and understanding the essence of living systems.
Google drive : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HUvhZy7Qaozi8xe5mjZd7_2-x9ToQr88/view?usp=drive_link
Studocu: https://www.studocu.com/row/u/128889644?sid=550504221748700246
Slide Share: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/biophysics-chapter-5-biomoelculat-structure-pdf/279960548
Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides: The Blueprint of Life
Nucleic acids and nucleotides form the molecular foundation of genetic information in all living organisms. From storing hereditary material to synthesizing proteins, these biomolecules are central to the structure and function of life itself.
In this post, we break down the structure, types, and functions of nucleotides and nucleic acids, and highlight their clinical significance in health and disease.
🧬 What Are Nucleotides?
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks (monomers) of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide consists of three components:
-
Nitrogenous base – Purines (Adenine, Guanine) or Pyrimidines (Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil)
-
Pentose sugar – Ribose (in RNA) or deoxyribose (in DNA)
-
Phosphate group
When multiple nucleotides join together via phosphodiester bonds, they form a nucleic acid strand.
📚 Types of Nucleic Acids
-
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
-
Double-stranded helix
-
Stores genetic instructions
-
Found in the nucleus (and mitochondria)
-
-
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
-
Usually single-stranded
-
Involved in protein synthesis
-
Types include mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and miRNA
-
🔁 Functions of Nucleic Acids
-
Genetic Information Storage – DNA stores the instructions for development, function, growth, and reproduction.
-
Protein Synthesis – RNA transcribes and translates the genetic code into functional proteins.
-
Energy Transfer – ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a modified nucleotide, is the main energy currency of the cell.
-
Cell Signaling – Certain nucleotides act as messengers (e.g., cAMP in hormone signaling pathways).
🔍 Clinical and Nursing Relevance
Understanding nucleic acids and nucleotides is essential in modern medicine and nursing practice:
-
Genetic Disorders – Mutations in DNA can lead to inherited diseases (e.g., sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis).
-
Cancer Biology – DNA damage and repair mechanisms are critical in cancer development and treatment.
-
Diagnostic Tools – PCR and genetic testing rely on DNA/RNA principles.
-
Pharmacology – Many drugs (e.g., antivirals, chemotherapy agents) target nucleic acid synthesis or function.
🧪 Fun Fact: ATP – A Special Nucleotide
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide that stores and transports chemical energy within cells. It powers muscle contractions, nerve impulses, and biosynthetic reactions—making it a molecular fuel for nearly all biological activity.
Conclusion
Nucleotides and nucleic acids are much more than biological jargon—they are the molecules of life. Their structure and function are deeply intertwined with every aspect of health, development, and disease. Whether you’re studying biochemistry, genetics, or clinical sciences, a solid understanding of these molecules is a must.
Google Drive : https://drive.google.com/file/d/175ZkB2syC4F5_RmR0utZZBD0rcQV3Ucq/view?usp=sharing
Studocu : https://www.studocu.com/row/u/128891266?sid=550504221748700968
Slide Share: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/nucleotides-nucleic-acids-notes-for-biophysics-and-biochemistry/279961200
Read More:
https://nurseseducator.com/didactic-and-dialectic-teaching-rationale-for-team-based-learning/
https://nurseseducator.com/high-fidelity-simulation-use-in-nursing-education/
First NCLEX Exam Center In Pakistan From Lahore (Mall of Lahore) to the Global Nursing
Categories of Journals: W, X, Y and Z Category Journal In Nursing Education
AI in Healthcare Content Creation: A Double-Edged Sword and Scary
Social Links:
https://www.facebook.com/nurseseducator/
https://www.instagram.com/nurseseducator/
https://www.pinterest.com/NursesEducator/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/nurseseducator/
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Afza-Lal-Din
https://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=F0XY9vQAAAAJ
Terrific article! That is thhe type of info that
should be shared acrosss the net. Shame on the search engines for not positioning thgis publish upper!
Come on over and seek advice frrom my website . Thank you =) https://fortune-glassi.Mystrikingly.com/